Dec 08 2010
Windows Blue Screen Analysis
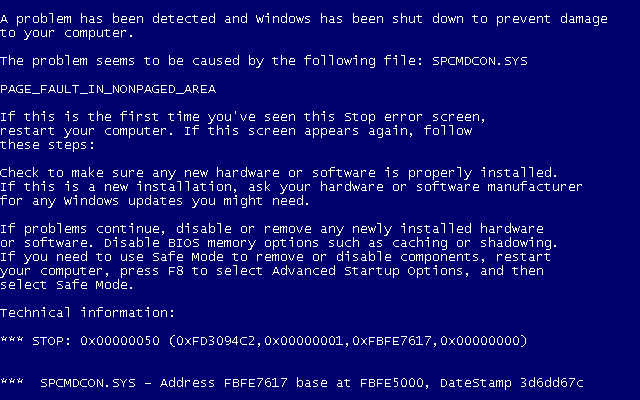
Despite what you may hear from Microsoft defenders, blue screens still occur in Windows family servers. After the system crash – hence the blue screen – Windows generates a memory dump file in C:/Windows/Minidump. The filename provides the date and time, a useful piece of information that lets you know about the crash frequency. These minidumps are also useful to conduct some Windows blue screen analysis.
Enable Blue Screen Minidumps
Minidumps should be enabled by default on your system but it is worth checking if you experience blue screens and C:/Windows/Minidump remains empty.
From the control panel:
– Go in System
– Click on “Advanced” tab
– Start and Recovery -> Settings
– Enable “Write an event to the system log”
– Disable Automatically restart
– Select the following debug info:
* Small memory dump (64 Kb)
* Small Dump Directory : %SystemRoot%\Minidump
Confirm settings on every window and restart the server.
Reproduce Windows Crash
Do whatever it takes to make Windows crash. If you do not know how to reproduce, blue screen dumps will add up in the minidump folder overtime and you can analyse them anytime later on.
Install Debugging Tools for Windows
The “Windows debugging tools” provides utilities for dump analysis. You can download them on Microsoft website.
MiniDumps Analysis
Now, you will need to extract information out of the minidump file. kd is the command we will use from the debugging tools for Windows to analyse blue screen dumps.
Open a command prompt window (Start -> Run -> “cmd”)
cd \program files\debugging tools
rem (Or the chosen path when you installed the Windows debugging tools)
kd -z C:\WINDOWS\Minidump\Mini???????-??.dmp
kd> .logopen c:\debuglog.txt
kd> .sympath srv*c:\symbols*http://msdl.microsoft.com/download/symbols
kd> .reload;!analyze -v;r;kv;lmnt;.logclose;q
You now have a debuglog.txt file in c:\, which you can open with Notepad or any text editor.
Conclusion
If you’re lucky enough, you may find the the program or driver name causing the blue screens in the MODULE_NAME and IMAGE_NAME modules. Knowing this, you can now fix the problem.